Page 2 - e3242
P. 2
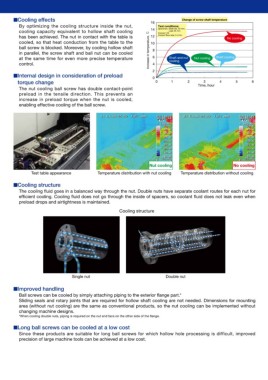
nCooling effects Change of screw shaft temperature
By optimizing the cooling structure inside the nut, 16
cooling capacity equivalent to hollow shaft cooling
has been achieved. The nut in contact with the table is Increase in temperature, : Test conditions: No cooling
cooled, so that heat conduction from the table to the
ball screw is blocked. Moreover, by cooling hollow shaft 14 Specimen; Shaft dia. 50 mm,
in parallel, the screw shaft and ball nut can be cooled Lead 25 mm
at the same time for even more precise temperature Coolant; Oil
control.
12 Coolant flow rate; 3 L/min
nInternal design in consideration of preload
torque change 10
The nut cooling ball screw has double contact-point 8
preload in the tensile direction. This prevents an
increase in preload torque when the nut is cooled, 6 Shaft and nut Nut cooling Shaft cooling
enabling effective cooling of the ball screw. cooling
4
2
0 234 5 6
01 Time, hour
Test table appearance Nut cooling No cooling
Temperature distribution with nut cooling Temperature distribution without cooling
nCooling structure
The cooling fluid goes in a balanced way through the nut. Double nuts have separate coolant routes for each nut for
efficient cooling. Cooling fluid does not go through the inside of spacers, so coolant fluid does not leak even when
preload drops and airtightness is maintained.
Cooling structure
Single nut Double nut
nImproved handling
Ball screws can be cooled by simply attaching piping to the exterior flange part.*
Sliding seals and rotary joints that are required for hollow shaft cooling are not needed. Dimensions for mounting
area (without nut cooling) are the same as conventional products, so the nut cooling can be implemented without
changing machine designs.
*When cooling double nuts, piping is required on the nut end face on the other side of the flange.
nLong ball screws can be cooled at a low cost
Since these products are suitable for long ball screws for which hollow hole processing is difficult, improved
precision of large machine tools can be achieved at a low cost.